MedInria is a free medical imaging software developed at Inria. MedInria aims at providing to clinicians state-of-the-art algorithms dedicated to medical image processing and visualization. MedINRIA is a free collection of softwares developed within the Asclepios research project. It aims at providing to clinicians state-of-the-art algorithms dedicated to medical image processing and visualization. Efforts have been made to simplify the user interface, while. MedINRIA is a platform containing a set of softwares. These modules have been developed by the INRIA research team Asclepios at Sophia Antipolis, France. This project was initiated by Pierre Fillard (PhD student at Asclepios) and Nicolas Toussaint (intern at Asclepios). New super mario bros switch.
Contents



Medinria Install
SHANOIR Software: a software package to share neuroimaging data
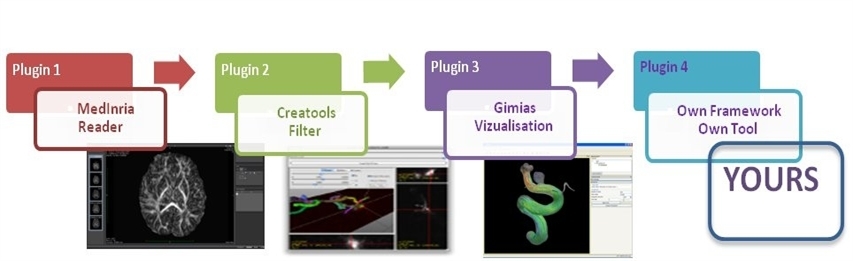
Empenn is taking part in the Inria development action around medInria. We are developing medInria, a software platform aimed at providing research clinicians with medical image analysis tools coming from research. This software will progressively include developments coming from 3 of the major teams in medical image analysis at Inria: Epione, Athena and Empenn, making it a future major diffusion platform for our research developments. More details on the medInria website.
Medinria Github
Based on MATLAB and the SPM8 toolbox, autoMRI provides complete pipelines to pre-process and analyze various types of images (anatomical, functional, perfusion, metabolic, relaxometry, vascular). A new version of the ASL post-processing part was developed in Python and Nipype, therefore not requiring the disponibility of Matlab licences.
Medinria Dti
Abstract
Medinria Download
Abstract. Processing and visualization of 3D medical data is nowadays a common problem. However, it remains challenging because the diversification and complexification of the available sources of information, as well as the specific requirements of clinicians, make it difficult to solve in a computer science point of view. Indeed, clinicians need ergonomic, efficient, intuitive and reactive softwares. Moreover, they need new solutions to fully exploit their data, but they often cannot access state-ofthe-art methods as those are mostly available in complicated softwares. The MedINRIA software was born to fill this lack and consists of a collection of tools that optimally exploit various types of data (e.g., 3D images, diffusion tensor fields, neural fibers as obtained in DT-MRI). Add-x unika driver. It provides state-of-the-art algorithms while keeping a user-friendly graphical interface. For each of these tools, we first introduce its dedicated application and the processing methods it contains. Then, we focus on the features that make interactions with data even more intuitive. Med-INRIA is a free software, available on Windows, Linux and MacOSX. Other MedINRIA tools are underway to make cutting edge research in medical imaging rapidly available to clinicians. The interest clinicians have shown in MedINRIA so far indicates that the need of such simple, yet powerful softwares is real and increasing. 1

